Digital transformation through RPA
Digital Transformation has become a fast-paced environment harboring the rise of new technologies, innovations, and ways of working. To stay competitive, companies must adapt to today’s business challenges and find ways to identify and adopt the game-changers in the technology stream.
An emerging trend is to utilize automation to perform business as usual tasks – from processing invoices, e-mails, contracts, and documents by extracting the relevant information, to the implementation of intelligent programs that can identify patterns and perform the appropriate actions. The technology supporting these scenarios is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). It is at the core of the digital transformation to help businesses improve their processes, automate repetitive tasks, and stay ahead of their competitors.

What is RPA?
RPA is technology-based automation of business processes governed by business logic and structured inputs. RPA makes use of workflow automation tools, combining the power of scripting tools, where a software developer writes a set of instructions that can be performed as a backend process and replication of actions taken into a graphical user interface (GUI). The latest represents most of the initial RPA initiatives. It lowers the barrier to create automation since “bots” (the computational agents developed in RPA) simply replicate a set of actions that the user would take.
The scenarios under the RPA umbrella range from sending e-mails, processing transactions, manipulating data, establishing communication between multiple systems, or triggering actions. Depending on the context, several levels of complexity may exist, driven by the predictability of the task, the requirement for human approval, and the level of abstraction in the decision-making process. According to these variations, there can be four categories of bots: unattended, attended, integration, and intelligent bots (increasing order of complexity).
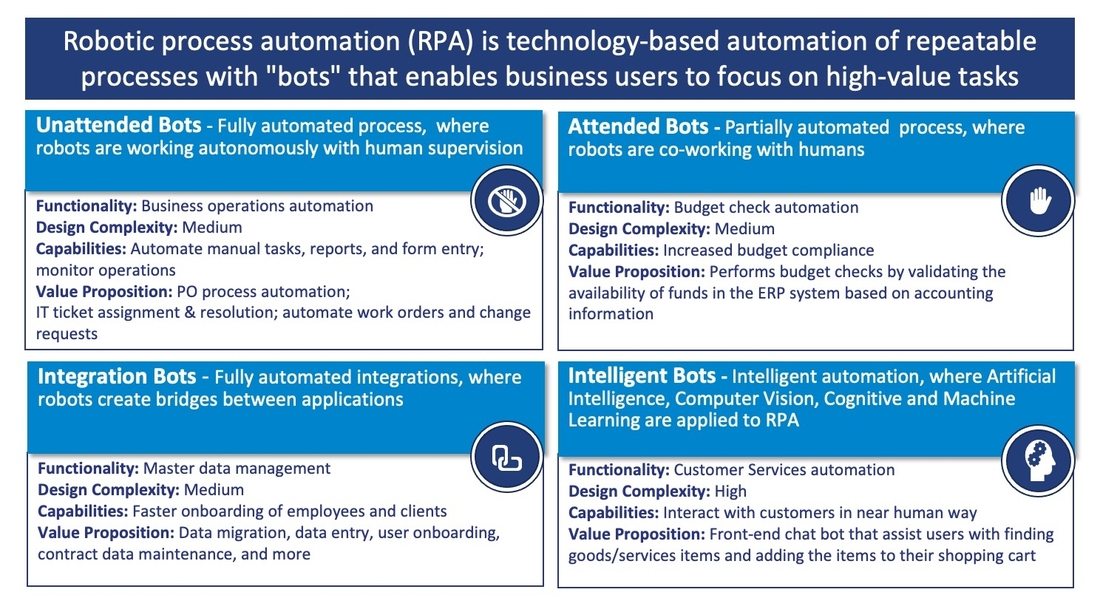
Businesses can use RPA in various tasks, such as extracting information from PDF or scanned documents, generating, reply and forward e-mails, creating/sending invoices, automatizing HR onboarding processes, payroll automation, or information validation. RPA versatility is not only present in its applications. It also drives process re-engineering to ensure accurate, well-documented, optimized, and automatized processes that enable faster and more reliable transactions, resulting in increased revenues – this is the core principle of RPA initiatives.
Processes with higher complexity, such as master data management, are also typical candidates for RPA implementations. The scope of automated processes in MDM goes beyond assisted migrations, as it can support keeping the single source of truth a golden record. RPA tools can handle large volumes of data, are easy to scale, and can ingest, analyze, enrich and process all the data available in the MDM systems, providing a foundation for a truly data-driven organization.
Business benefits of RPA
The typical benefits of robotic automation include reduced cost, increased speed, accuracy, and consistency, improved compliance & service quality, scalability of production, and providing a gateway to AI and advanced analytics (Figure 2). When coupled with tools like CyberArk, automation can also provide a security layer. It will allow bots access, particularly sensitive data and information from a password vault without requiring human workers to manage passwords or have direct access to this content (which is relevant for cases like clinical trials or fields like finances).
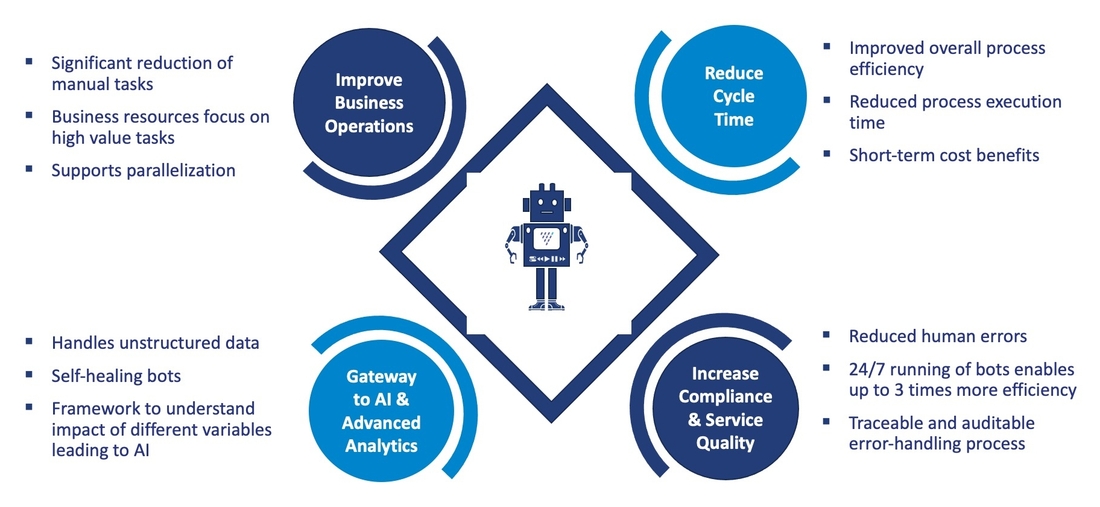
Considering this context, the core of the RPA business case relies on its ability to provide organizations with the ability to reduce staffing costs and human error. Through tools like UI Path, Automation Anywhere, or Blue Prism, bots usually are quick to develop, easy to integrate, and cost-effective to produce, requiring no deep system integrations or additional software. Enhancing RPA with cognitive technologies such as machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP) or speech recognition enables the bots to perform higher-order tasks that generally require human judgment, in an unsupervised way.
To conclude, RPA reduces staffing costs while increasing productivity and efficiency by releasing employees to do other tasks rather than repetitive work. RPA also works as a gateway for project management methodologies like Agile. Most automation can start with a controlled scope and then be iteratively improved in a continuous delivery/continuous integration (CD/CI) model to ensure business continuity, more immediate benefits, and controlled cutover processes.
Conclusion
Many companies are starting to understand the real potential of RPA to improve the efficiency of their end-to-end processes while increasing their digital transformation footprint. Finding the right candidates to apply automation and their extent, scoping the critical path of this technology is a unique exercise for each business stream. In this RPA series, we will highlight how different process streams (supply chain, order-to-cash, master data management, analytics) can benefit from automation, what synergies exist, and how this technology can shape the path for the enterprises of the future. Is your company ready for Robotic Process Automation?
Contact our industry experts at Tenthpin if you would like to learn more.
Stay up to date with the latest #Lifeattenthpin #LifeSciences #Pharma #MedDevices #Biotech #Digitalforlife #Thoughtleadership #Medical Technology #AnimalHealth news by following us on Instagram #LifeAtTenthpin Facebook Tenthpin and our Tenthpin LinkedIn corporate page.

